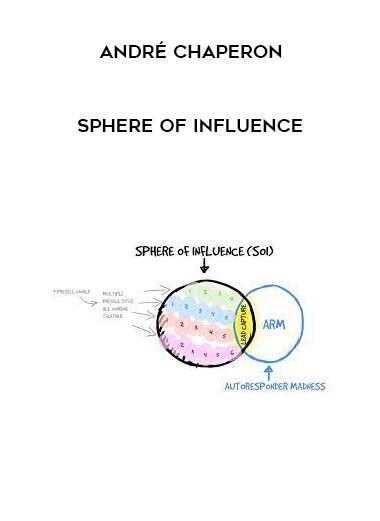
Courses Infomation
Trauma-Informed First Responder Training by Melinda Gronen

Trauma-Informed First Responder Training by Melinda Gronen
**More information:
Description
You’re an integral part of your community; always first to run toward dangerous and unpredictable situations where traumatized citizens are likely part of the equation.
But first responders and law enforcement have often been left out of the trauma conversation. Without proper training on handling trauma in the field safety risks, misunderstandings, and missed opportunities can keep you from doing your job and increase the potential for liability.
This webcast will provide you the skills, tools and techniques you need to identify psychological trauma, properly engage citizens with mental health issues, manage their challenging behaviors, and de-escalate emergency situations more effectively than ever before. And our experienced trainers will provide you with the tools you need to overcome your own struggles when the tragedies you see start to take their toll.
Real-world case examples from two decades of experience responding to critical incidents will show you how you can:
- Better protect both public and personal safety
- Apply crisis communication strategies during critical moments
- Deescalate and engage citizen cooperation
- Spend less time managing aggressive, reactive, or avoidant behaviors
Register today and get the training you need to safely and effectively respond to trauma in your work!
Can’t Miss Topics!
- Better protect public and personal safety
- Quickly deescalate situations and engage cooperation
- Crisis communication techniques for people in survival mindset
- Build your resilience and stay on the job
Psychological Trauma Overview
- Definition of stress and trauma
- Types of trauma people experience
- Impacts on physical and mental health (Adverse Childhood Experiences Study)
- Limits of current research and first responder response
Red Flags for First Responders: How to Identify People Who’ve Experienced Trauma
- Neurobiological survival responses – Fight/Flight/Freeze/Fawn
- When the survival “alarm” is broken
- Psychological stages of trauma
- Challenging behaviors and trauma
The Trauma-Informed Toolbox: Increase Safety, Communication and Cooperation
- Understand cognitive capacity in crisis
- Create a situational alliance
- Utilize crisis communication strategies
- Promote a sense of safety and avoiding escalation of the crisis
- Develop community connections and responses pre and post crisis response
The Self Care Go-Bag: Effective Ways to Help Yourself and Help Your Peers
- Know the signs that someone is in crisis
- Assessing your “baggage” in the field
- Understand your triggers
- Know your strengths and challenges
- Where to go for help
Case Studies
- Sammie – 14-year old female with a long history of abuse and challenging behaviors
- Ms. Hawkins – 28-year old mother of an 8-year old female; requesting intervention
More information about Medical:
Medicine is the science and practice of establishing the diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and prevention of disease.
Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness.
Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease,
typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.
Medicine has been around for thousands of years, during most of which it was an art (an area of skill and knowledge) frequently having connections to the religious and
philosophical beliefs of local culture. For example, a medicine man would apply herbs and say prayers for healing, or an ancient philosopher and physician would apply bloodletting according to the theories of humorism.
In recent centuries, since the advent of modern science, most medicine has become a combination of art and science (both basic and applied, under the umbrella of medical science).
While stitching technique for sutures is an art learned through practice, the knowledge of what happens at the cellular and molecular level in the tissues being stitched arises through science.
Salepage : Trauma-Informed First Responder Training by Melinda Gronen
About Author
<author content>









![Peter Titus - Create Your Own Automated Stock Trading Robot In EXCEL! [39 Video (MP4) + 2 Document (HTML)]](https://crablib.info/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/Peter-Titus-Create-Your-Own-Automated-Stock-Trading-Robot-In-EXCEL-39-Video-MP4-2-Document-HTML.jpg)



















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.